History lectures by Dr. Steve Blankenship of Georgia Highlands College.
- Subject:
- History
- World Civilization
- Material Type:
- Lecture
- Author:
- Steve Blankenship
- Date Added:
- 11/26/2019

History lectures by Dr. Steve Blankenship of Georgia Highlands College.

This course introduces the history of Africa from 300,000 BCE to the era of European imperialism in the nineteenth century. The story continues in HIST 252, which covers the last 120 years of African history. Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: locate major regions, geographic features, and populations in Africa and label them on a map; identify major events and trends in the history of Africa prior to 1890 that describe change over time; demonstrate the impact of the African environment on human history in Africa and explain how humans in turn changed that environment; compare and contrast the diverse social and political structures and systems devised by Africans; summarize the connections between Africans and other peoples of the world and the ways in which those connections changed over time; demonstrate the usefulness, best practices, and limitations of different types of sources for understanding the African past; appraise various conceptions of the African past given the evidence from that past; assess the degree to which there can be said to be one, shared African history before 1890. This free course may be completed online at any time. (History 251)

The history of economic thought represents a wide diversity of theories within the discipline, but all economists address these three basic questions: what to produce, how to produce it, and for whom. The student will learn that without a clear sense of the discussions and debates that took place among economists of the past, the modern economist lacks a complete perspective. By examining the history of economic thought, the student will be able to categorize and classify thoughts and ideas and will begin to understand how to think like an economist. Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: Explain and analyze the development of economics as a discipline in various ancient cultures; Trace the development of European economic thought and analyze concepts in historical context; Compare and contrast Classical economic theories; Synthesize the elements of Neo-Classical and Keynesian approaches in the modern era; Evaluate the merits of alternative approaches to maximizing happiness. (Economics 301)

This course will introduce the student to the history of Europe from 1800 to present day. The student will learn about the major political, economic, and social changes that took place in Europe during this period including Industrial Revolution, the First and Second World Wars, imperialism, and the Cold War. By the end of this course, the student will understand how nationalism, industrialization, and imperialism fueled the rise of European nation-states in the nineteenth century, as well as how world war and oppressive regimes devastated Europe during the 1900s. Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to: Think critically and analytically about European history in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries; Identify and analyze the varying causes and effects of the Industrial Revolution in Europe; Identify, describe, and analyze the development of a coherent set of ideologies in post-Napoleonic Europe: liberalism, socialism, Marxism, nationalism, and Romanticism; Identify and describe the causes and effects of the era of reform and revolution in Europe in the 1820s and 1830s, as well as analyze the Revolutions of 1848; Describe and analyze the effects of urbanizationĺÎĺĚ_ĺÜexpanding cities, rising public health risks, redefined social classes, the evolving nature of the family, and new developments in science and thought; Identify the age of nationalism in Europe between 1850 and 1914. Students will analyze FranceĺÎĺĺÎĺs Second Empire, ItalyĺÎĺĺÎĺs unification, GermanyĺÎĺĺÎĺs unification, and the modernization of Russia. Students will also be able to define the emergence of the modern nation-state during this period; Identify the causes and characteristics of EuropeĺÎĺĺÎĺs ĺÎĺĺĺŤNew ImperialismĄ_ĺĺö of the late nineteenth century. Students will also be able to describe and analyze responses to this imperialism in Africa, India, the Middle East, and the Far East; Assess how and why World War I erupted in 1914. Students will also be able to identify and describe the characteristics and impact of the Great War; Identify and describe the Russian Revolution of 1917, including the fall of the Romanov dynasty and the Bolshevik Revolution; Identify and describe the cultural and social problems that characterized post-WWI Europe. Students will be able to analyze Modernism, ethnic and economic problems in central and eastern Europe, and the Great Depression; Identify and describe the rise of authoritarian regimes in Europe during the 1920s and 1930s. Students will be able to analyze Stalinism, Fascism, and Nazism; Identify and describe the causes and conflicts of World War II. Students will also be able to analyze, identify, and describe the Holocaust; Analyze and explain the Cold War. Students will also be able to analyze, identify, and describe the collapse of Communism and the Soviet Union, as well as the end of the Cold War; Identify and describe the post-WWII social transformations in Europe, including the rise of feminism, the rise of counterculture, and new developments in both science and technology; Analyze and interpret primary source documents from the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, using historical research methods. (History 202)
Brief video describing where and how to find Open Educational Resources, including specific repositories and licences to look for.
"The Human Controller" presents and discusses design and evaluation issues of human-machine interaction. The focus is on understanding human perception-action couplings (limitations, preferences, adaptation) and on quantifying control behavior of humans in the direct manual control loop of vehicles, robots or other man-made tools. Case studies from automotive, aviation, medical and tele-operation applications are discussed, with a special focus on the importance of including and enhancing haptics (=the sense of touch) during manual control.
Relation of purpose of data to data requirements. Relation of data to costs.
Accuracy requirements of measurements and error propagation:
Related to a problem the required accuracy of measurements and the consequences for accuracy in the final result are discussed. Different types of errors are handled. Propagation of errors; for dependent and independent measurements, from mathematical relations and regression is demonstrated. Recapitulated is the theory of regression and correlation.
Interpretation of measurements, data completion: By standard statistical methods screening of measured data is performed; double mass analysis, residual mass, simple rainfall-runoff modelling. Detection of trends; split record tests, Spearman rank tests. Methods to fill data gaps and do filtering on data series for noise reduction.
Methods of hydrological measurements and measuring equipment: To determine quantitatively the most important elements in the hydrological cycle an overview is presented of most common hydrological measurements, measuring equipment and indirect determination methods i.e. for precipitation, evaporation, transpiration, river discharge and groundwater tables. Use, purpose and measurement techniques for tracers in hydrology is discussed.
Advantages and disadvantages and specific condition/application of methods are discussed. Equipment is demonstrated and discussed.
Areal distributed observation: Areal interpolation techniques of point observations: inverse distance, Thiessen, contouring, Kriging. Comparison of interpolation techniques and estimation of errors. Correlation analysis of areal distributed observation of rainfall
Design of measuring networks: Based on correlation characteristics from point measurements (e.g. rainfall stations) and accuracy requirements the design of a network of stations is demonstrated.

In dit college wordt een introductie gegeven van een groot aantal facetten van de scheepshydromechanica en hun onderlinge samenhang zoals die later in de studie meer als geisoleerde onderwerpen aan bod komen. Behandeld worden: de hydrostatica, de geometrie beschrijving van het schip, inleiding lijnenplan, het begrip stabiliteit, de stabiliteit van drijvende lichamen, eenvoudige stabiliteit berekening bij kleine helling hoeken, de weerstand van lichamen onder water en aan het oppervlak, eenvoudige weerstand benaderings methoden voor schepen, de model wetten in de hydromechanica, de extrapolatie methode van Froude, de lift van een vleugel, de vleugel karakteristieken, de toepassing hiervan bij voortstuwing en bij scheepsschroeven, de schroef karakteristieken en een eenvoudige schroef berekening, en tenslotte de fysica van het zeilen en zeilvoortstuwing. Leerdoelen De student kan: 1. de basis van systeem analyse beschrijven (buitenwereld, interfaces, beperkingen, objecten, relaties enz.) 2. maritieme systemen zoals schip/motor/schroef beschrijven en modelleren met behulp van beperkte systeem analyse methodologie; eenvoudige maritieme systemen modelleren door onderverdeling in subsystemen en componenten 3. evenwicht condities van maritieme systemen bepalen en kwalitatief analyseren 4. de definities en belangrijkste karakteristieken van weerstand, voortstuwing en manoeuvreren (snelheid, weerstand, vermogen, RPM, draaicapaciteit) begrijpen en toepassen 5. de relaties tussen algemeen vloeistof dynamica en scheepshydromechanica (bijv. lift/aerodynamica/zeilen; visceuze stroming/Reynolds getal/volgstroomvelden/voortstuwingsrendement; laminair & visceuze stroming/weerstand; niet visceuze stroming/golf patronen/weerstand) beschrijven 6. de achtergrond van de belangrijkste schaal regels (Newton, Froude, Reynolds) d.m.v dimensie analyse uitleggen 7. schaalregels voor schaalmodel experimenten in een sleeptank toepassen en potentiĚÇle complicaties identificeren
Fenomenologische beschrijving van de stroming om een schip classificatie van weerstandscomponenten en parametrische methoden voor de berekening van de scheepsweerstand. Daarnaast wordt uitgelegd hoe de scheepsweerstand experimenteel bepaald kan worden.
Voor scheepsschroeven wordt aangegeven hoe de complete geometrie beschreven kan worden, hoe de stuwkracht en koppel uit een parametrische beschrijving kan worden berekend m.b.v. een systematische schroevenserie en via een ideaal stromings model (actuator schijf). Een introductie in cavitatie (vorming van waterdamp gebieden) is onderdeel van de cursus.

This 4-lecture series covers the basics of the immune system, how T cells work, how MHC proteins affect our susceptibility to autoimmune diseases, and the relationship between the immune system and infectious diseases.

This course will introduce the student to organizational psychology, or the application of psychological research and theory to human interaction in the workplace. Industrial/Organization Psychology takes research findings and theories that were originally used to explain general human behavior and applies them to human behavior in the workplace. The course begins by taking a look at how the student evaluates jobs and employees before exploring how the student evaluates and motivate employees, noting what encourages versus discourages employee job commitment. The student will then study leadership and group influences in the workplace, including working conditions, humans factors, performance management, and work teams. Leadership interaction and the leadership theories are also covered. Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: perform a thorough and systematic competency model (job analysis); develop and validate a job specific selection design; design, develop, and evaluate a job specific training program; define a performance appraisal process and form; identify research methods for conducting experiments; explain organizational recruitment, selection, and retainment; evaluate the work performance of employees; describe the motivating factors of employees; identify teamwork problems and issues; compare and contrast models of motivation and leadership; explain organizational issues including: teams, attitudes, and occupational health; define work-life balance and its impact on organizations and employees. (Psychology 304)

Hoofdpunten: De cursus geeft een kennismaking met infrastructuur voor Watermanagement. Voor Waterbeheer ligt de focus op ontwatering, afwatering, wateraanvoer en het ontwerpen van eenvoudige aan- en afvoersystemen. Voor Civiele gezondheidstechniek ligt de focus op Gezondheidstechniek en volksgezondheid, drinkwatervoorziening en Integraal waterbeheer. Leerdoelen: Begrip van basisopzet infrastructuur Watermanagement. Eenvoudige systemen kunnen ontwerpen.
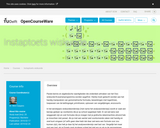
Parate kennis en algebraĚřsche vaardigheden die onderdeel uitmaken van het Vwo wiskunde B-examenprogramma worden opgefrist. Hierbij moet gedacht worden aan het handig manipuleren van goniometrische formules, bewerkingen met logaritmen, toepassen van de kettingregel, primitiveren, oplossen van vergelijkingen, enzovoorts.
Single lecture presentation containing tips for using technology to enhance teaching. Uses proven multimedia design principles to enhance learning.
This set of instructor-focused ancillary materials was created under a Round Eleven Mini-Grant for Ancillary Materials Creation and Revision. These following materials are intended to assist instructors in successfully implementing OpenStax Sociology 2nd Edition within their classrooms:
Customizable lecture slides
Links to potential ancillary Web materials for each chapter
Short answer questions
Essay questions
Online discussion questions
Class activities
The course Intelligent User eXperience Engineering (IUXE) is given for the master programme 'Media and Knowledge Engineering' and for students from other master programmes. The aim is to achieve an understanding and practical experience of key principles, methods and theories in the area of intelligent user experience engineering. Study Goals: Knowledge of a basic, coherent approach for developing software systems in such a way that the systems' users can accomplish their goals effectively and efficiently, and with a high level of satisfaction. Knowledge of new theories and methods for improving the user experiences in the development of intelligent systems, and of research approaches to enhance the theoretical and empirical foundation of IUXE methods. Practical experience in an iterative human-centered development process, i.e. the application of theories and methods for the generation and testing of intelligent user interfaces. This process comprises the generation of a design with its rational, and user experience testing with video analysis, logging and data analyses tools.
In this course, the student will build on and apply what you learned in the introductory macroeconomics course. The student will use the concepts of output, unemployment, inflation, consumption, and investment to study the dynamics of an economy at a more advanced level. As the course progresses, the student will gain a better appreciation for how policy shifts and changes in one sector impact the rest of the macroeconomy (whether the impacts are intended or unintended). The student will also examine the causes of inflation and depression, and discuss various approaches to responding to them. By the end of this course, the student should be able to think critically about the economy and develop your own unique perspective on various issues. Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: Explain the standard theory in macroeconomics at an intermediate level; Explain and use the basic tools of macroeconomic theory, and apply them to help address problems in public policy; Analyze the role of government in allocating scarce resources; Explain how inflation affects entire economic systems; Synthesize the impact of employment and unemployment in a free market economy; Build macroeconomic models to describe changes over time in monetary and fiscal policy; Compare and contrast arguments concerning business, consumers and government, and make good conjectures regarding the possible solutions; Analyze the methods of computing and explaining how much is produced in an economy; Apply basic tools that are used in many fields of economics, including uncertainty, capital and investment, and economic growth. (Economics 202)
This course is designed to extend the student's knowledge of the basic microeconomic principles that will provide the foundation for their future work in economics and give them insight into how economic models can help us think about important real world phenomena. Topics include supply and demand interaction, utility maximization, profit maximization, elasticity, perfect competition, monopoly power, imperfect competition, and game theory. Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: Explain the standard theory in microeconomics at an intermediate level; Explain and use the basic tools of microeconomic theory, and apply them to help address problems in public policy; Analyze the role of markets in allocating scarce resources; Explain both competitive markets, for which basic models of supply and demand are most appropriate, and markets in which agents act strategically, for which game theory is the more appropriate tool; Synthesize the impact of government intervention in the market; Develop quantitative skills in doing economic cost and consumer analysis using calculus; Compare and contrast arguments concerning business and politics, and make good conjectures regarding the possible solutions; Analyze the economic behavior of individuals and firms, and explore how they respond to changes in the opportunities and constraints that they face and how they interact in markets; Apply basic tools that are used in many fields of economics, including household economics, labor economics, production theory, international economics, natural resource economics, public finance, and capital markets. (Economics 201)

In this course, the student will learn fundamental principles of international law and examine the historical development of these laws. The first half will define international law, identify its foundations, and review its historical development. The student will examine one of the most central debates of international law: how these laws are enforced -- or, in many cases, not enforced. The inherent conflicts of international law with national sovereignty, domestic politics, and balance of power will also be reviewed. This course will explore specific topics within international law, such as the laws of war, the laws of the sea, international human rights, international crimes, environmental law, protection of intellectual property, and international trade. Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: explain how international law has developed over time; discuss the difficulties in enforcement of international law; identify issues that international law seeks to resolve; demonstrate an understanding of how power and politics influence the formation, application, and enforcement of international law; assess the effectiveness of international law in resolving transnational disputes. (Political Science 412)

This course will introduce the student to the field of international political economy, teaching students the ways in which economics and politics influence each other when it comes to creating policy. Economic policy can be an important instrument of statecraft and diplomacy between countries, yet countries can also use economic policy to punish or express disapproval towards other countries using sanctions. In this course, the student will learn about the international organizations and regimes that are designed to facilitate international economic transactions and ensure economic stability, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF). The student will also review the impact that globalization has on the world economy and the gap between rich and poor countries. Upon successful completion of this course, the student will be able to: identify, explain, and compare major theories in the field of international political economy; analyze the effects of trade policies on domestic and international actors; evaluate the costs and benefits of Foreign Direct Investment and Sovereign Debt; explain the development of the international currency system and analyze the effects of domestic policies; compare and contrast approaches to human rights and access to basic human needs. (Political Science 411)